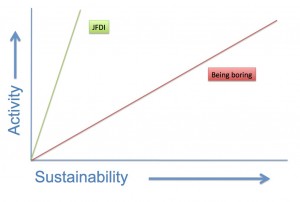
A question was asked in the social media community of practice (various levels of authentication required) about using web 2.0 technology to support learning. I couldn’t help myself…
Blogging
Using blogs to record and share learning is a really nice use of technolog. Blogging is great for writing stories and sharing experience, especially when everyone in an organisation can access and search the information on a blog. Fundamentally blogs are just really easy ways of getting content online, but the personal nature of them also helps individuals write about their own knowledge and learning. Get people to blog about a recent learning experience they have had, or about tips and tricks that they have come across in their work that others could make use of.
Forums
One of the things we have come across at Learning Pool when it comes to e-learning is that when people can talk to others about something, it tends to stick in their minds much better than when they just read about it. So our e-learning management system provides forums along with courses so that those studying that lessons can ask questions of the rest of the learning community, discuss the content and work together on problems. Forums can also be used to support face to face training and learning activity too – enabling people to talk to each other about what they learned in the classroom afterwards, helping to make that learning stick in their heads, and to clear up any confusions people might have walked away with!
Wikis
Blogs are good for people to record their personal learning experiences, and forums for having conversations about learning, but what about building collections of resources for people to refer to, and add to, over time? For that you need a more traditionally structured website, but one which lots of people can contribute to. That’s where wikis come in. Any kind of useful web resource, where large groups of people can contribute material, is great for a wiki. Rather than handing out loads of sheets of paper during a training session, why not put them all up on a wiki for people to access online? That way everyone always gets the latest version, and if there’s is something that needs correcting or updating, someone from the community can do it for you. Alternatively, wikis are great for building online dictionaries or jargon busters, for example.
It might be considered a distraction to have people sat in a training sessions fiddling away with their phones, but actually having people recording and sharing what they are finding out is a great way to learn! It’s just like taking notes with paper, only everyone can re-use it. If you use a common hashtag with your training, everything that has been tweeted during the sessions can be drawn together in one place and everyone can benefit from it. Even better, by using a public platform like Twitter, you can get people not present in the training giving their input too, adding to the mix of ideas.
Media sharing
A great way for people to consolidate learning is to record training sessions and let them watch, or listen to them again later on. It’s simple enough to record a video of a talky bit of training using a Flip or Kodak video camera and then share it either publicly on the web or on an intranet, say. Alternatively, audio podcasts might be easier to do and share. Other resources can be shared online too, whether presentations using a public site like Slideshareor other documents and learning materials on Scribd. By sharing this stuff publicly, others can take what you have done and add bits and improve it in places and everyone can benefit. To see an example of this, check out this fantastic resource from the Scottish Government Library Services.
Social bookmarking
Sites like Delicious, which let you store links to useful web pages and sites on a public webpage are a great way for a group of learners to share the great stuff they find online. Once you get into the habit of bookmarking interesting articles using a social bookmarking tool, it becomes a quick and easy way to build up huge knowledge bases of related content. Using tagging to build up your own vocabulary of key words to describe content makes bringing together resources on a similar topic really fast too.
Social networks
Using social network type features, as seen on Facebook and others, is a really useful way of combining a lot of the activity above with a great method of further sharing people’s knowledge, talents and interests. Social networks tend to feature Twitter-like status updates, discussion boards and media sharing (but generally not wikis, sadly). What they also have is user profiles which are great ways for people in an organisation to share details of what they know about, what they do, what they are interested in and where there talents lie. So much more useful than the traditional ‘yellow pages’ style staff directories! So if you need some expertise on an issue, someone to lead a training session maybe, if you have an internal social network you could search and find the ideal person.

 This glossary of social media and digital engagement terms comes from a recent piece of my strategy work. It’s skewed towards the government sector, in terms of language and examples. Feel free to use any of this that might be useful for other purposes. Or to challenge my definitions. Or, perhaps, to add glaring things I’ve missed. There are probably no definitive answers to some of these, but I hope you find them interesting and thought-provoking.
This glossary of social media and digital engagement terms comes from a recent piece of my strategy work. It’s skewed towards the government sector, in terms of language and examples. Feel free to use any of this that might be useful for other purposes. Or to challenge my definitions. Or, perhaps, to add glaring things I’ve missed. There are probably no definitive answers to some of these, but I hope you find them interesting and thought-provoking.