(Previously published on LinkedIn and in my newsletter.)
Following on from previous posts during the Great Local GDS Flurry from a few weeks ago (has everyone else moved on? Well I haven’t!), I thought I would follow up on one of my ideas for what I see as the central problems facing local authorities wanting to make the most of digital (by which I mean: technology, data, and online experience). Those problems are capacity and capability.
An answer to those problems is sharing of services. Now shared services often have a bad rep (in a lot of cases they are neither shared nor a service). But that doesn’t mean the model can’t work. It just means you have to do it right, and that doesn’t mean munging two or three teams together, sacking a couple of managers, then bagging the savings and carrying on exactly as before.
The right way is to methodically plan what functions are suitable for sharing, that will deliver benefits like efficiency and economies of scale, and not forcing into a shared arrangement something that just doesn’t belong there – or at least, not yet.
It strikes me that Wardley mapping could be very helpful here. I’ve been a massive fan of the approach for years, but have never actually used it in anger, largely because my brain is too small to cope with it. Here’s a video where Simon calmly explains it all.
The broad points are this:
- There are no one size fits all approaches to any kind of business capability, but especially not technology ones
- The more established and commoditised a capability, the better suited it is to things like shared services or outsourced arrangements
- The more innovative a capability, the more suited it is to being kept close to the organisation
- Likewise, the closer a capability is to affecting the experience of your end user, the closer you want to keep it to the organisation. If it is back-end gubbins, then that’s more suitable to being handled by someone else.
- It is also possible for capabilities to move as they mature or become commoditised. So the way things are today don’t have to be the way they are tomorrow.
OK! So bearing that in mind, how could we think about applying this thinking to digital capabilities within a Council?
I’ve produced a dumbed down Wardley map to help guide this thinking. It isn’t comprehensive by any means, but hopefully has enough in it to get the point across!
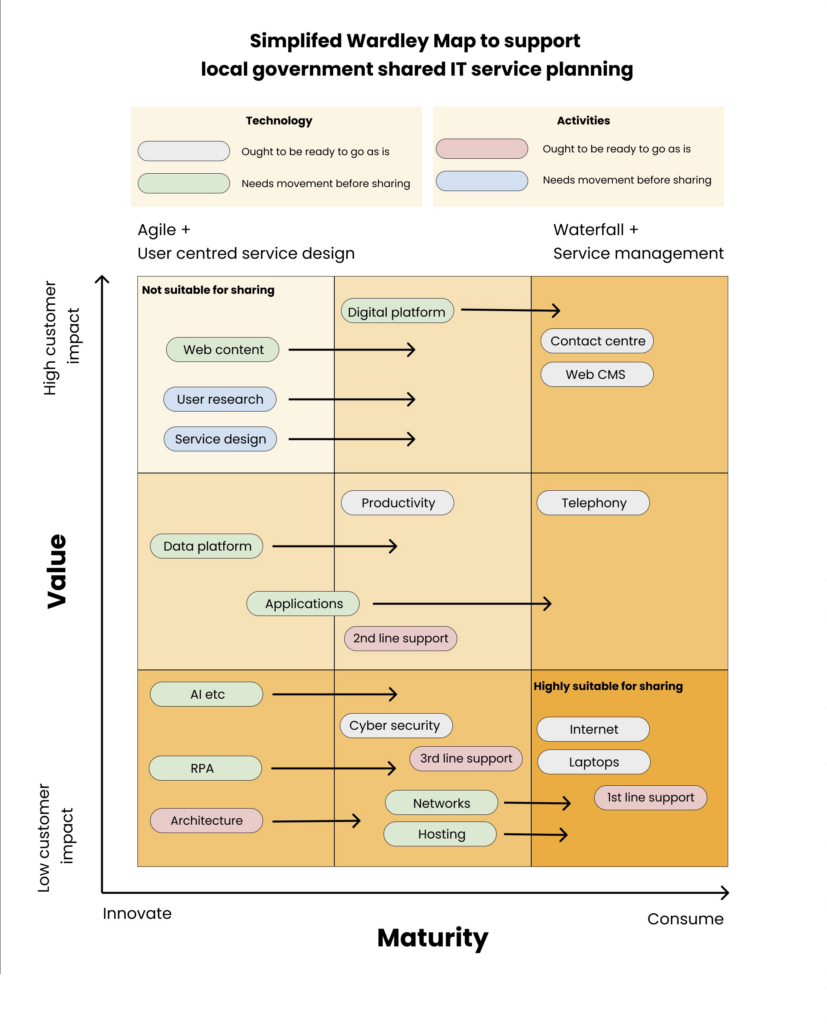
I find having a grid approach helps organise my thoughts around this a bit. It means you lost a bit of the elasticity of the original Wardley approach, and if you find that annoying, no worries! You don’t have to do this the same way I do.
So the darker orange box in the bottom right is where sharing of digital capabilities ought to start on day one. These are utility-like components that have little impact on the end user and where real economies of scale can be achieved by organisations joining together.
After that, councils could start exploring the other boxes, depending on their context and ambition. There are some areas that should be left well alone, at least until they can be shifted rightwards in some way – either the market and the organisation’s experience matures, or the organisation is able to change the way it works to facilitate a rightward shift for that thing.
Now, we could all have an arm wrestle about which of these capabilities fits in what box, and I dare say that some local customisation will be required depending on context (some councils have insanely complicated bespoke arrangements around laptop builds, for example). But it feels like a handy tool to use when planning collaborative endeavour, whether formal shared services or not.
It would be great to know what you think!
